WHAT IS ZINC?
Zinc is a chemical substance that is abundant in the Earth’s crust. It is a bluish-white metal with excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. Additionally, zinc is a vital mineral for both humans and animals and is involved in many biological processes. Its excellent bioavailability and possible health advantages make it a popular dietary supplement. Zinc is well-known for its ability to improve immunological function, facilitate wound healing, and help in the absorption of other minerals.
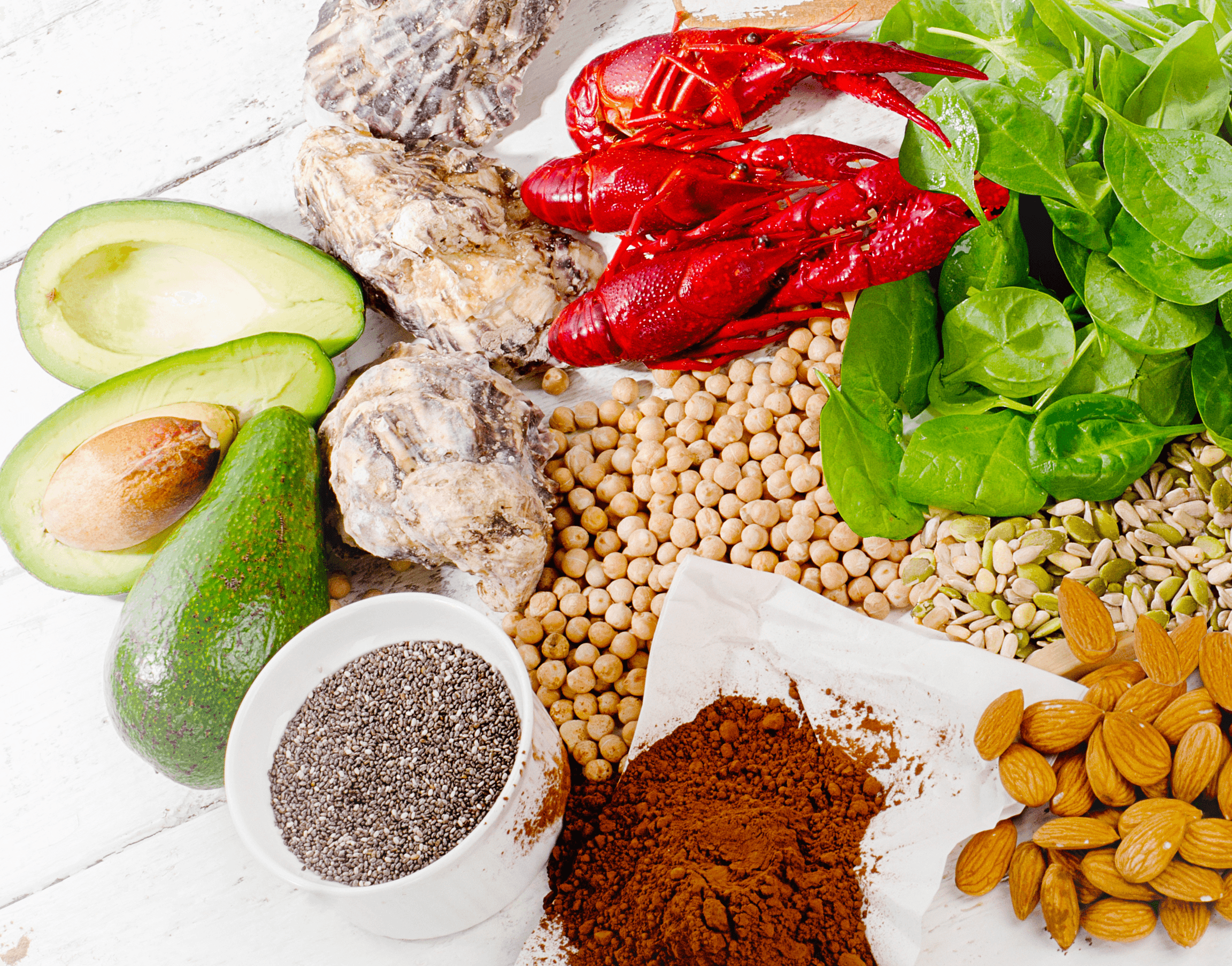

WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF ZINC ?
The benefits of supplementing Zinc include:
- May improve immunity: Zinc is a common ingredient in over the counter (OTC) drugs and natural therapies because of its ability to build up the immune system and reduce inflammation. As a result, if given when symptoms first arise, it might potentially help treat some types of infections. Additionally, zinc may function as an antioxidant, lowering inflammation and guarding against long-term illnesses including diabetes, cancer, and heart disease. A study of 28 trials found that zinc supplementation may even prevent symptoms and lessen the severity of some respiratory tract infections.
- May improve blood sugar: Zinc is known for its function in insulin secretion and blood sugar regulation. Insulin is the hormone in charge of carrying sugar from your bloodstream to your tissues. According to some study, zinc may help maintain consistent blood sugar levels and increase your body’s sensitivity to insulin. According to additional studies, zinc may help lower insulin resistance, which would enhance your body’s capacity to utilise insulin effectively and maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
- May reduce acne: Zinc supplements have been used to enhance skin health and cure common skin problems such as acne. It has been shown that zinc sulphate is particularly effective at reducing the signs and symptoms of mild to severe acne. One research found that zinc supplements might lessen the typical number of inflammatory bumps brought on by acne, in addition to the fact that persons with acne typically have lower blood levels of zinc than people without the condition. Due to its low cost, high effectiveness, and significantly lower adverse effects, zinc supplements are often picked over alternative forms of therapy.
However, there is plenty of proof that Zinc benefits the human body in many ways, but pretending as your own doctor can be harmful. It can be dangerous, therefore always check your doctor or a healthcare professional before including Zinc supplements into your supplement diet.
HOW DOES ZINC WORK IN HUMAN BODY?
According to a few surveys and studies, optimal dietary zinc consumption is required for healthy growth and development during pregnancy, as well as in early childhood, formative years, and adulthood. In addition, zinc may be necessary for spermatogenesis and normal sperm physiology, pancreatic beta-cell function, and glucose absorption, as well as appropriate immune cell formation, activity, and function in both innate and adaptive immune systems (e.g., sperm motility).
Zinc ions suppress N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors within the brain, which is relevant to depression because this condition is characterised by increased glutamatergic neurotransmission (to which NMDA receptors contribute), and zinc supplementation has been demonstrated in some research to have antidepressant properties. Moreover, zinc deficiency has been linked to poor cognitive function as well as an increased risk of neurodegenerative disorders including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Zinc may also help with depression by raising levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor.
HOW MUCH ZINC CAN A PERSON TAKE?
The dosage of zinc you should take per day is determined by your food intake as well as the type of supplement you pick, as various supplements contain varying levels of elemental zinc. For example, Zinc citrate contains around 11% zinc by weight: The elemental zinc in 439 mg of zinc citrate is 50 mg. The recommended daily intake of zinc citrate for adults is reportedly between 8 and 11 mg of elemental zinc, or possibly more if necessary. It is crucial to remember that exceeding the prescribed amount might cause nausea, vomiting, and copper deficiency.
It is often advised to adhere to the manufacturer’s recommendations or seek out specific advice from a healthcare provider. Also, it’s critical to remember that taking more zinc than is advised each day might have adverse implications, so it’s vital to be aware of your overall intake of zinc through food and supplements.
WHAT ARE THE VARIATIONS OF ZINC?
Zinc is also available as:
- Zinc Acetate Nutrition Grade (~29% Zn)
- Zinc Aspartate Trihydrate Nutrition Grade (~25% Zn)
- Zinc Bisglycinate Nutrition Grade (~20% Zn)
- Zinc Citrate Nutrition Grade (~31% Zn)
- Zinc Gluconate Granular Nutrition Grade (~13% Zn)
- Zinc Gluconate Powder Nutrition Grade (~13% Zn)
- Zinc L-Carnosine Nutrition Grade (~21% Zn)
- Zinc Lactate Dihydrate Nutrition Grade (~22% Zn)
- Zinc Malate Trihydrate Nutrition Grade (~25% Zn)
- Zinc Monomethionine Nutrition Grade (~18% Zn)
- Zinc Orotate Nutrition Grade (~14% Zn)
- Zinc Oxide Nutrition Grade (~80% Zn)
- Zinc Picolinate Nutrition Grade (~21% Zn)
- Zinc Pidolate (Zinc PCA) Nutrition Grade (~19% Zn)
- Zinc Sulphate Heptahydrate Nutrition Grade (~21% Zn)
- Zinc Sulphate Monohydrate Nutrition Grade (~35% Zn)
Zinc is commonly available in:
- Zinc tablets
- Zinc capsule
- Zinc gummies
Glentworth Formulations is here to suit your every need. Everything from Tablets, Capsules and Powder blends.
If you are wanting to know more information, please get in contact with us. Either using the contact form or contacting us directly on: [email protected].


